Advanced options strategy knowledge
Short Put Condor
Short Put Condorcan consist of either a call option contract or a put option contract.
The two different contract types make up two hawk-style spread combinations: Short Put Condor and Short Call Condor.
Take Short Put Condor as an example. If you expect the stock price to fluctuate slightly, but are unsure about the direction of the stock price fluctuation, and want to achieve profits at a low cost and with controlled risk under such circumstances, you can use selling an hawk-style put option.
How to build
Short Put Condor consists of four options trades
● Sell 1 copy of put1
● Buy 1 copy of put2
● Buy 1 copy of put3
● Sell 1 copy of put4
The underlying assets and expiration dates of Put1, Put2, Put3, and Put4 are all the same. The differences are:
Exercise price: put1<put2<put3<put4, put2-put1=put4-put3
Strategy brief
Short Put Condor. Normally, opening a position is to sell an imaginary value put1 with a low interest price, buy an imaginary value put2 with a low to medium price, buy a real value put3 with a medium to high bid price, and sell a real value option put4 with a high interest price.
The difference between the exercise price of the two real value puts is equal to the spread of the two imaginary value puts, and the distance between the two exercise prices in the middle can be adjusted flexibly according to market conditions.
Of course, you can also choose the execution price spread of four puts at equal intervals.
The underlying asset and maturity date of all options are the same.
In this strategy, selling put1 and put4 is the main trading part to fulfill investors' expectations that “the stock price is expected to fluctuate greatly in the future”. Buying put2 and put3 is mainly used to control the risk of put1 and put4.
Generally, when sShort Put Condor, when opening a position, the premium income obtained by selling put1 and put4 will be higher than the option premium expenses for buying put2 and put3. Therefore, at the beginning of strategy construction, the strategy showed a net inflow on the book, and the cost of opening a position using this strategy was relatively low.
Short Put Condor is a combination of limited profit and loss.
When the stock price is higher than the highest exercise price or lower than the minimum exercise price, the strategy generates the greatest return, which is the combined net option premium income.
When the stock price is between the two intermediate exercise prices, the strategy makes the biggest loss, subtracting the lower exercise price for the medium to low option price and then subtracting the net premium income.
It is important to note that this strategy requires trading 4 options to open and close positions, and the transaction cost is relatively high.
Furthermore, the maximum profit of the strategy is the net option premium, so the price effectiveness of the option during the opening period is important to avoid a mismatch between the option price that is unfavorable to oneself and the option value when opening a position.
Risks and benefits

● Break-even point
Low break-even point: stock price = low exercise price+net option premium
High break-even point: stock price = high exercise price - net option premium
● Maximum profit
Net option premium income
● Maximum loss
Maximum loss = medium to low exercise price - low exercise price - net option premium income
Examples of calculations
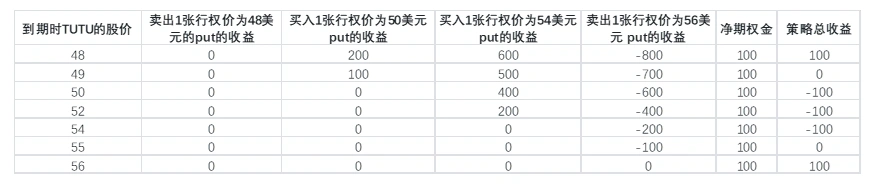
Assuming that in the US stock market, TUTU's current stock price is 52 US dollars. You think TUTU's stock price will fluctuate greatly in the next month, but you don't know the direction of fluctuation. If you want to achieve low cost and risk-controlled profits under such expectations, you can use Short Put Condor.
Sell 1 put with an exercise price of 48 US dollars at the price of 1 US dollar;
Buy 1 put with an exercise price of 50 US dollars at a price of 2 US dollars;
Buy 1 put with an exercise price of 52 US dollars at a price of 4 US dollars;
Sell 1 put with an exercise price of 56 US dollars at a price of 6 US dollars;
At maturity, your earnings will be as follows:
Explanation:
1. The article uses stocks as option targets to explain strategies. The actual investment bid can also be stock indices, futures contracts, bonds, currencies, etc.;
2. Unless otherwise specified, all options in this article refer to on-market options;
3. The TUTU company in the article is a virtual company;
4. The relevant calculations in this article do not take into account handling fees. In actual options investment, investors need to consider transaction costs.





